Upcoming Virtual dSTORM Training – Coming January 29, 2026 register now>
- Applications
Extracellular Vesicles
Exosomes and other extracellular vesicles (EVs) play key roles in cell-to-cell communication. EVs can cross biological barriers (such as the blood-brain barrier) and get internalized into the cell with a high degree of specificity. Thus, they are an ideal candidate for novel drug delivery methods and disease diagnostics.
About Extracellular Vesicles
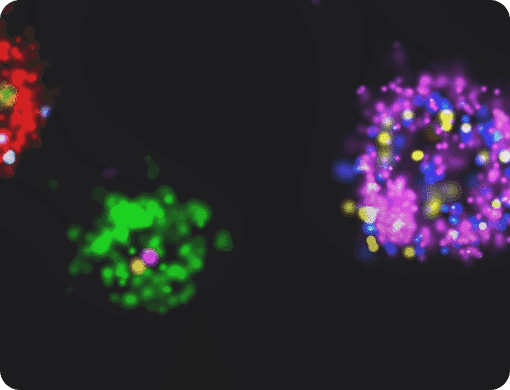
Challenges in visualizing extracellular vesicles
A substantial and growing body of evidence highlights extracellular vesicles as critical components in cell-to-cell communication pathways. The visualization of EVs is fundamental to our understanding of the role of EVs in all aspects of cellular transmission; from the packaging of signaling molecules and nucleic acids during vesicle biogenesis, to tracking of their uptake and fate after internalization within selected target cells or tissues.
As EVs vary greatly in both size and protein content, it is believed that the presence of specific biomarkers (including tetraspanins, integrins and other proteins) on different sub-groups of EVs may be the root cause of this selectivity. However, characterizing these biomarkers on individual EVs poses a significant challenge to researchers in the field.
While electron microscopy techniques have the capability to resolve individual EVs, they do not easily allow detection of multiple markers at the same time, and are limited to fixed cells. Super-resolution microscopy surpasses the resolution barrier of conventional light microscopes and enables detection and quantification of single proteins and nucleic acids at the sub-vesicular level.
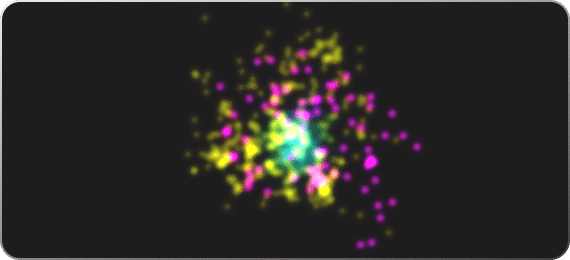
Characterize EVs with super-resolution
Super-resolution microscopy can be used to visualize and identify EVs in cells and in solution. Biomarkers can be stained in single EVs, each with a different fluorescence signature. By using one generic marker of EVs (like ONI’s Pan-EV stain) in one color and specific markers for EVs (such as CD9, CD63 and CD81) in others, it is possible to study the fraction of EVs with a particular biomarker within a population, confidently gaining insights on both single EVs and on the population.
In addition to imaging EV dynamics within live cells, single-molecule fluorescence microscopy can be used to follow the trajectories of fluorescently labeled vesicles in solution through nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA); a tracking-based analysis of the brownian motion of single particles. NTA calculates the rate of particle movement, known as the diffusion coefficient, and from here it estimates the size of the nanoparticles. These features of NTA provide quantitative information on the properties of EVs in solution, namely size and concentration, which explains the wide adoption of NTA in the EV research community.
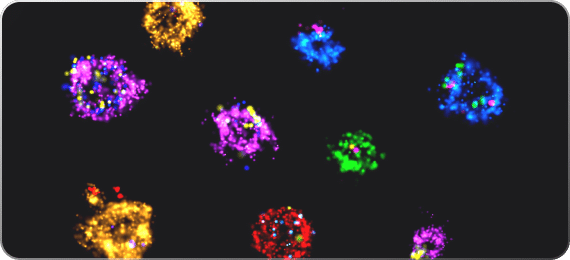
Size, count, image… understand
One of the most challenging aspects of studying EVs, and perhaps one of the most important, is combining multiple complementary characterization techniques. Single-molecule fluorescence microscopy offers the most sensitive fluorescence measurements available, allowing us to extract information with greater sensitivity than with any other tracking-based fluorescence instrument.
A special advantage of using a single-molecule super-resolution microscope is that it offers exceptional resolution for visualizing the same population of EVs in cells and in solution. For instance, identifying the production of EVs in cells, isolating them and categorizing them with tracking data, and finally, adding them back to cells to investigate their biological function by visualizing their interaction with cellular components. The imaging could even involve live cells: studying uptake by time-lapse SIM imaging at high resolution, or real-time tracking to study the interaction of EVs with the target cell membrane. Alternatively, it could involve fixing cells after sufficient time for the EVs to be taken up, and using 20 nm resolution dSTORM microscopy to study the interaction of EVs with molecules in the target cells (e.g. lysosomes, endocytic markers) at unprecedented resolution.
Isolated EVs in solution can also be permeabilized and their content can be further analyzed to detect biomarkers. Thanks to the high sensitivity of super-resolution microscopy, even small sub-populations can be successfully identified.
Case Studies
ATP1A3 as a target for isolating neuron-specific extracellular vesicles from human brain and biofluids
In this paper, the scientists aimed to investigate the potential of the protein ATP1A3 to serve as a biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease progression in EVs isolated from neurons and from liquid biopsies. They used a number of methods to identify ATP1A3 as an EV biomarker specific to neurons. Additional single EV analysis reveals that ATP1A3 is specific and abundant in induced neurons from humans, and its levels in EVs correlate with levels of Alzheimer’s Disease-related proteins like Aβ. Since ATP1A3 is abundant in EVs derived from liquid biopsies, it can serve as a marker for neurodegenerative diseases.
Yang You et al. ,ATP1A3 as a target for isolating neuron-specific extracellular vesicles from human brain and biofluids.Sci. Adv.9,eadi3647(2023). DOI:10.1126/sciadv.adi3647
Extracellular vesicles from the lung pro-thrombotic niche drive cancer-associated thrombosis and metastasis via integrin beta 2
In this work, scientists set out to explore the mechanism behind thrombosis in cancer patients. They discovered a subpopulation of the immune cell macrophages that reside in the lungs and secrete small EVs that are enriched with the protein Integrin beta 2. This protein binds glycoproteins on the surface of platelets and coagulation proteins in the blood, initiating thrombosis. This work included single EV analysis on clinical samples from patients, and is an important first step in identifying at-risk patients, as well as in developing treatments.
Lucotti, S. et al. Extracellular vesicles from the lung pro-thrombotic niche drive cancer-associated thrombosis and metastasis via integrin beta 2. Cell 188, 1642-1661 (2025), DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.01.025.
Selenoprotein P is a target for regulating extracellular vesicle biogenesis and secretion from activated microglia in vivo
The researchers set out to study how the protein Selenoprotein P (sepp1) is involved in the regulation of EV secretion by microglia, the immune cells that guard the brain. They confirmed that sepp1 is important for normal EV production, and that its absence is affecting multiple EV characteristics, as well as other cellular pathways. Since EVs from microglial cells were shown to be involved in several neurological conditions, sepp1 can be a new drug target in patients.
Bodart-Santos V, Ruan Z, Melvin BC, Pandey I, Ikezu S, Ikezu T. Selenoprotein P is a target for regulating extracellular vesicle biogenesis and secretion from activated microglia in vivo. Cell reports. 2024 Dec 24;43(12), DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.115025
End-to-end EV workflow

Aplo Scope
A new era in super-resolution microscopy. Combine high-power SMLM imaging with low power live cell imaging across a expansive fully homogeneous FOV. Now powered by CODI, Aplo Scope increases experimental throughput with 5 color imaging capabilities and offers maximal spectral discrimination.

The Nanoimager
Discover the power of advanced super-resolution imaging with our compact benchtop microscope, designed to elevate your EV research. Featuring cutting-edge modalities like dSTORM, PALM, PAINT, Single-Particle Tracking, smFRET, TIRF, and HILO, this versatile system offers unparalleled imaging capabilities to explore and analyze extracellular vesicles in unprecedented detail.

EV Profiler 2
ONI Application Kit™: EV Profiler 2 is ONI’s advanced reagent kit for visualizing and phenotyping extracellular vesicles with dSTORM microscopy on the Nanoimager, offering enhanced reproducibility, improved EV capture efficiency, and precise sizing and colocalization of up to three biomarkers per EV, complemented by AutoEV software for automated, comprehensive analysis in just 90 minutes.
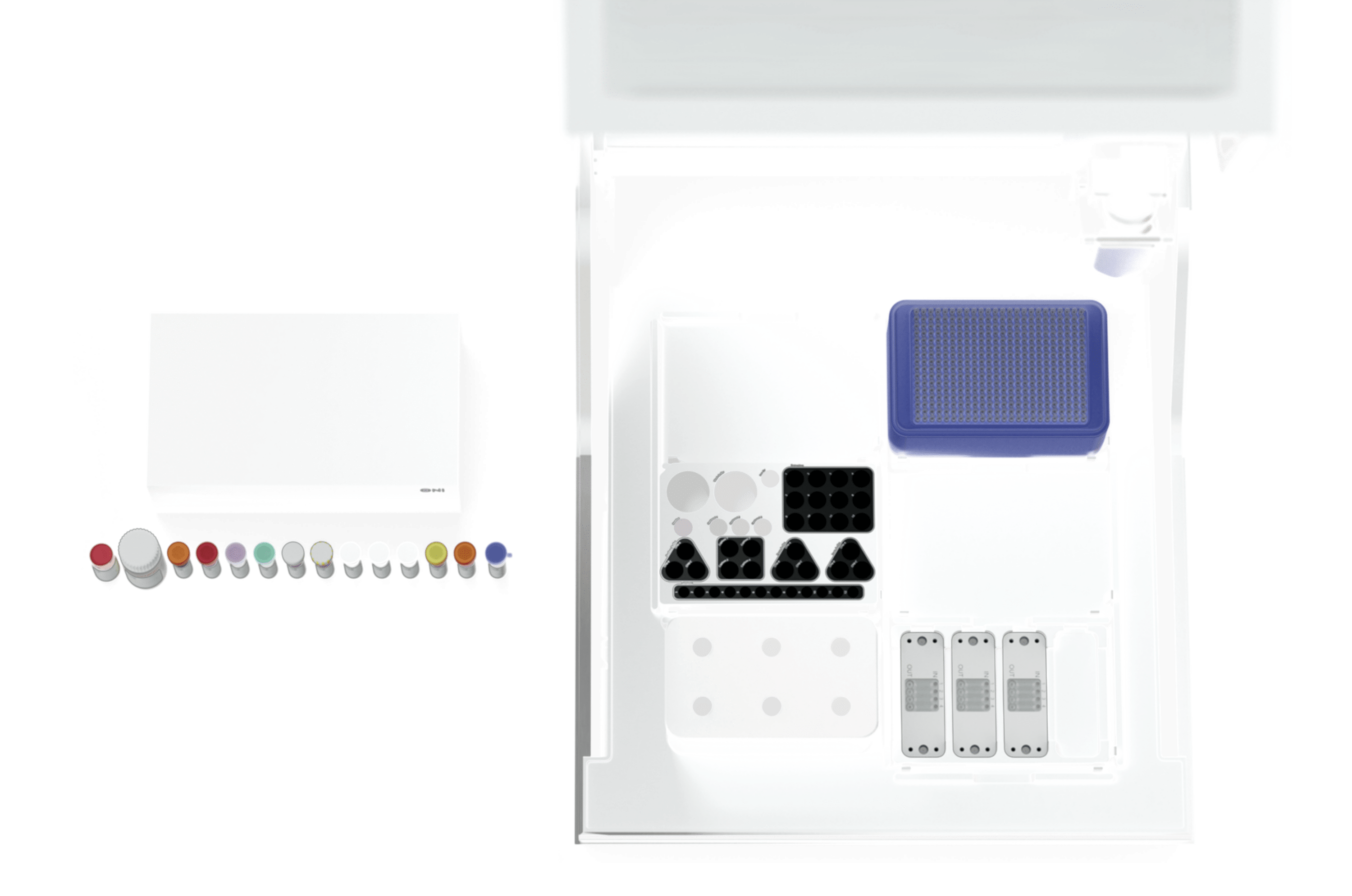
Aplo Flow
Achieve precision in EV research with our fully automated, customizable fluidics solution. Designed for reliable, reproducible sample preparation, it’s the most user-centric, end-to-end tool for super-resolution microscopy in extracellular vesicle studies.
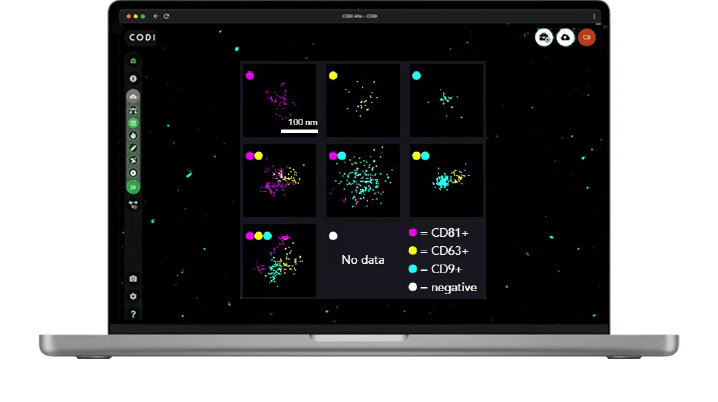
AutoEV in CODI
When combined with our newest software offering, AutoEV, your system will be calibrated and optimized to acquire and analyze a 4-lane chip automatically and deliver a comprehensive report of EV size and positivity for each individual lane in 90 mins.
Key Resources
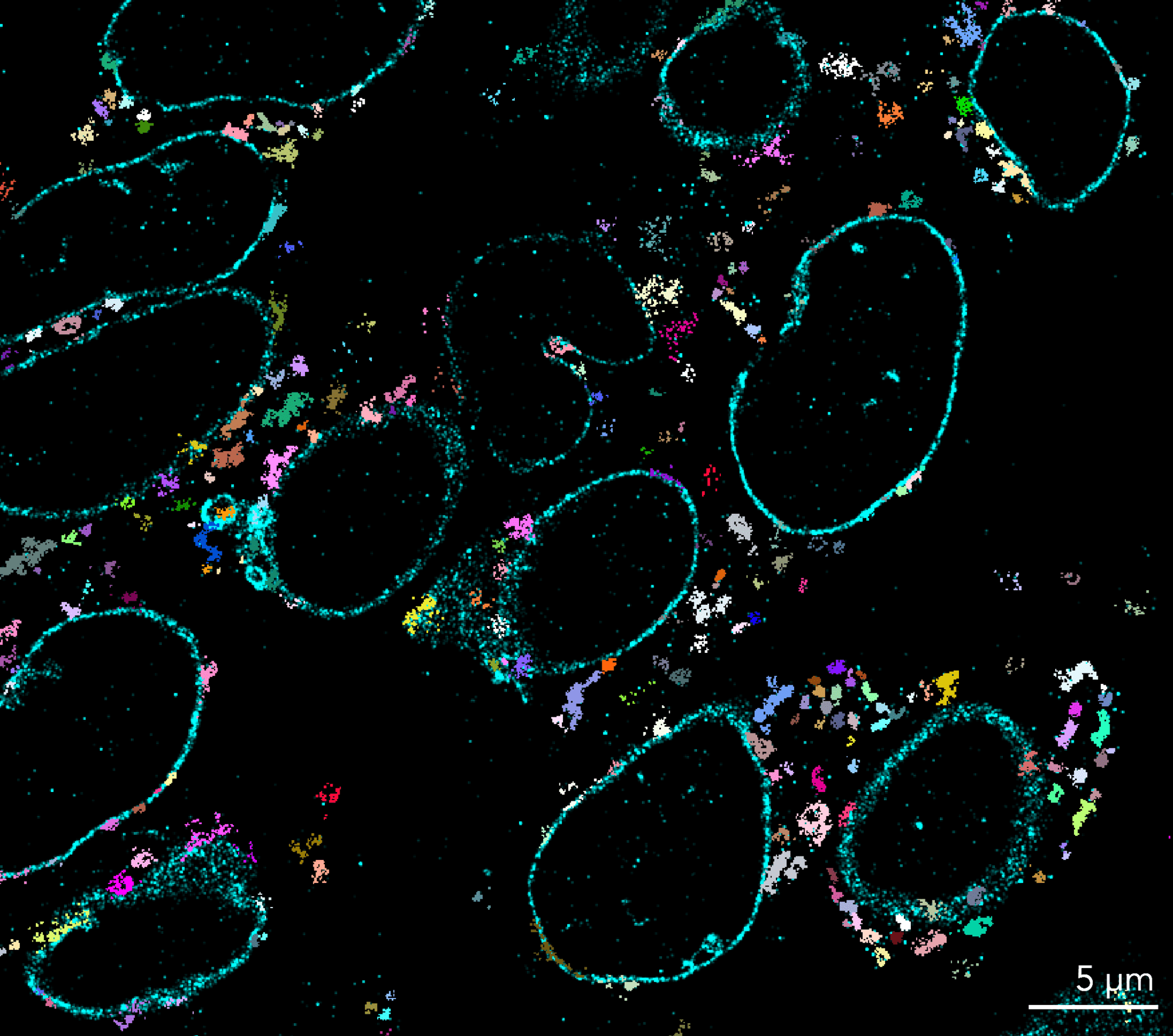
Gallery

















FAQs
The Nanoimager is a class 1 laser product that can be used in a standard lab, without specific laser training or the need for a dark room. Simply plug it in and image anywhere!
No, you can do a lot more. The Nanoimager allows you to investigate your sample using different imaging technologies on both fixed or live samples.
Yes. Our consumable kits largely simplify sample preparation and these can be compatible with other imaging systems with equivalent specifications. However, all our kits are optimized for use with the Nanoimager.